I. Introduction
In the vast realm of languages, English stands as a global lingua franca, a bridge that connects diverse cultures and communities. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of everything one needs to know about the English language, from its origins to its modern applications. We will delve into its structure, vocabulary, grammar, and its impact on the world stage.
II. Origins and Evolution
A. The Beginnings
English, as we know it today, has evolved over centuries. Its roots can be traced back to the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes who settled in what is now England around the 5th century. They brought with them a Germanic language, which later became Old English.
B. The Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest of 1066 introduced French vocabulary to the English language, particularly in the realm of government and law. This period marked the beginning of Middle English.
C. The Great Vowel Shift
The Great Vowel Shift, a series of changes in vowel pronunciation, occurred in the 15th century, which had a profound impact on the English language.
D. Modern English
The 16th and 17th centuries saw the development of Modern English, characterized by the influence of the printing press and the works of Shakespeare.
III. Structure and Phonetics
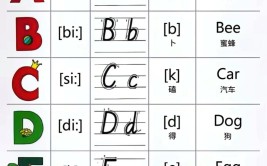
A. Alphabet and Vowels
The English alphabet consists of 26 letters, with five short vowels and five long vowels. The combination of these vowels and consonants creates the vast array of sounds that make up the language.
B. Phonetics and Phonology
Phonetics is the study of sounds, while phonology is the study of the organization of sounds in a language. English has a rich phonetic system that can be challenging for non-native speakers.
IV. Vocabulary and Dictionaries
A. Etymology
Understanding the etymology of words can provide insight into their origins and meanings. For example, the word \